Cooling towers are marvels of engineering that play a vital role in many industrial processes and large-scale air conditioning systems. These towering structures, often seen in industrial complexes, power plants, and even some large commercial برج خنک کننده, serve the crucial function of dissipating heat generated during various industrial processes or air conditioning systems.
Functionality and Design:
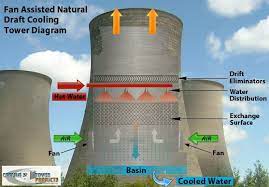
At their core, cooling towers work on the principle of evaporative cooling. Hot water or steam from industrial processes or air conditioning systems is circulated through the tower, where it comes into contact with a stream of air. As this air passes over the hot water, a portion of it evaporates, absorbing heat from the water and lowering its temperature. The cooled water is then circulated back into the industrial process or air conditioning system, while the warm, moist air is expelled into the atmosphere.
Cooling towers come in various designs, but the most common types include:
- Natural Draft Cooling Towers: These are massive structures characterized by their hyperbolic shape. They rely on the natural buoyancy of air to draw air upwards through the tower, creating a draft that enhances the cooling process. Natural draft towers are often used in large power plants and industrial facilities due to their high capacity and efficiency.
- Mechanical Draft Cooling Towers: Unlike natural draft towers, mechanical draft towers utilize fans or other mechanical means to draw air through the tower. They come in two main configurations: induced draft and forced draft. Induced draft towers have fans located at the top of the tower, which pull air upwards through the tower, while forced draft towers have fans located at the base of the tower, which push air upwards. Mechanical draft towers are commonly found in smaller industrial facilities and commercial buildings.
Applications:
Cooling towers find applications across various industries, including:
- Power Generation: In power plants, cooling towers are used to dissipate the heat generated during the electricity generation process. They are particularly common in coal, nuclear, and natural gas power plants, where large amounts of heat are produced during the generation of electricity.
- Chemical and Petrochemical Industries: Many chemical and petrochemical processes require precise temperature control. Cooling towers are used to remove excess heat generated during these processes, ensuring optimal operating conditions and product quality.
- Air Conditioning Systems: Large commercial buildings, such as shopping malls, office complexes, and hospitals, often use cooling towers as part of their air conditioning systems. These towers help regulate the temperature of the water used to cool the building, improving energy efficiency and reducing operating costs.
- Manufacturing Processes: Cooling towers are integral to various manufacturing processes, including steel production, food and beverage processing, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. They help maintain stable operating temperatures and prevent equipment overheating, ensuring consistent product quality and production efficiency.
Environmental Considerations:
While cooling towers play a crucial role in industrial processes and air conditioning systems, they also raise environmental concerns. One significant issue is the potential for water consumption and environmental impact. Cooling towers require a continuous supply of water for their operation, leading to significant water usage, especially in areas prone to water scarcity. Additionally, the warm water discharged from cooling towers can raise the temperature of nearby water bodies, impacting aquatic ecosystems.
To mitigate these concerns, many industries are adopting water-saving technologies, such as closed-loop cooling systems, which recirculate water within the system, reducing overall water consumption. Additionally, advancements in cooling tower design and operation are focused on improving energy efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
Conclusion:
Cooling towers are indispensable components of modern industrial processes and air conditioning systems. Their ability to efficiently dissipate heat plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating conditions and ensuring the reliability and efficiency of various industrial processes. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility, the development of innovative cooling tower technologies will play a vital role in reducing water consumption and minimizing environmental impact while meeting the growing demand for temperature regulation in a wide range of applications.